Concept, Example
A toolchain is the set of tools that compiles source code into executables that canrun on your target device, and includes a compiler, a linker, and run-timelibraries.
Components:
- Binutils: as, ld, addr2line, strip, string,…bin-utils link
- GNU Compiler Collection(GCC): compiler for C, Objective-C, C++, Java,..
- C library: API based on POSIX, which is the main interface to the OS kernel for Application
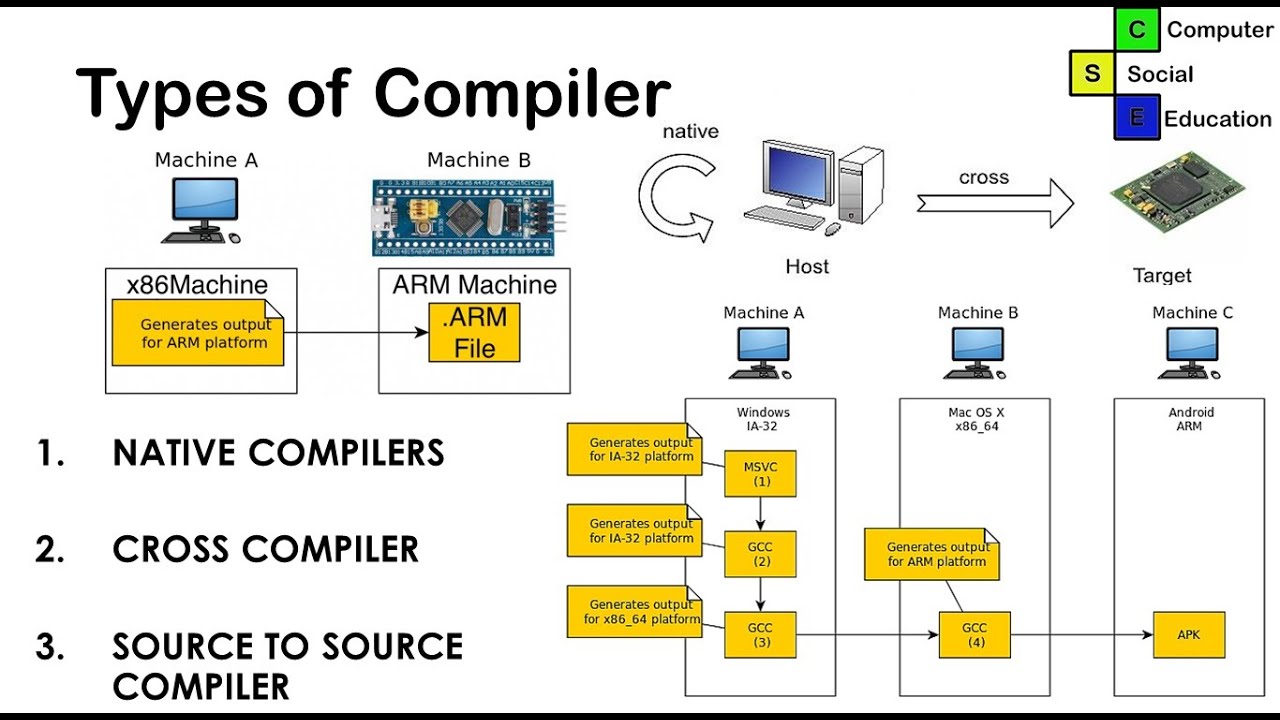
Type of toolchains:
- Native: this toolchain run on same type of target system
- Cross: build on host machine and run binary on other system.
some convention toolchain depened by CPU architectures:
Extended Application Binary Interface (EABI) Old Application Binary Interface (OABI) Extended Application Binary Interface Hard-Float(EABIHF) use floating point register
GNU uses a prefix to the name of each tool in the toolchain.
Ex: mipsel-unknown-linux-gnu-gcc, x86_64-linux-gnu,..
cmd gcc -dumpmachine
C library
Application -> C library -> Linux Kernel
C library will use systemcall to use services of the Linux kernel.
Several C library: glibc, musl libc, uClibc-ng( Linux for CPUs without MMU)
Buiding a toochain use Crosstool-NG
Note for C library: when use shared librarys the linker will look for shared object in default search path: /lib and /usr/lib. we can add LD_LIBRARY_PATH to add other search path for the shared library. LD_LIBRARY_PATH have higher priority than default search path.
