Scanning port, TCP & UDP, reliable data transfer, improvement in tcp
Outline
- Theory : 4 tubles value
- Scanning port
- Difference between TCP & UDP
- Principles of reliable data transfer
- ARQ Automaic Repeat reQuest protocols
- Conclusion
- Impovement in tcp
Theory: 4 tuples value
The transport layer at the server notes the following four values in the con-nection-request segment:
- the source port number in the segment
- the IPaddress of the source host,
- the destination port number in the segment
- its own IP address.
The newly created connection socket is identified by thesefour values; all subsequently arriving segments whose source port, source IPaddress, destination port, and destination IP address match these four values willbe demultiplexed to this socket.
When a TCP segment arrives at the host, all four fields (source IP address,source port, destination IP address, destination port) are used to direct (demultiplex)the segment to the appropriate socket
Scanning port
For TCP, nmap sequentiallyscans ports, looking for ports that are accepting TCP connections. For UDP, nmapagain sequentially scans ports, looking for UDP ports that respond to transmitted UDP segments. In both cases, nmap returns a list of open, closed, or unreachableports. A host running nmap can attempt to scan any target host anywherein theInternet
Difference between TCP and UDP
UDP require a minimum seding rate & without hand shaking step ( without the delay) UDP :No connection establishment UDP :No Connection state
UDP, on the other hand, doesnot maintain connection state and does not track any of these parameters. For this reason, a server devoted to a particular application can typically support manymore active clients when the application runs over UDP rather than TCP. Small packet header overhead.
The TCP segment has 20 bytes of header over-head in every segment, whereas UDP has only 8 bytes of overhead
Blocking UDP traffic for security reasons, TCP becomes an increasingly attractive protocol for streaming media transport.
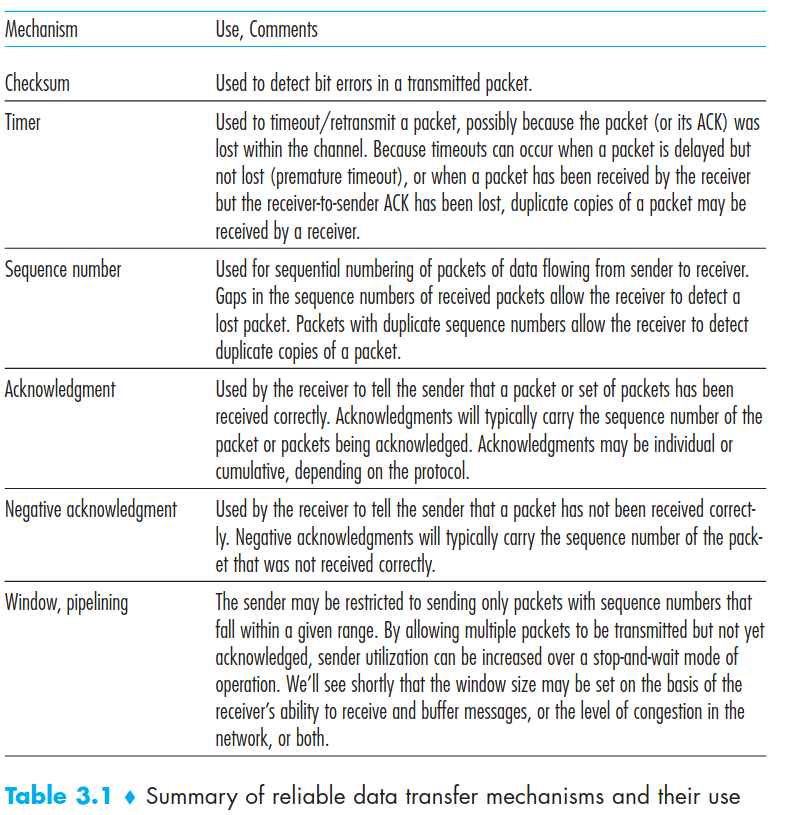
Principles of reliable data transfer
Reliable is implement on diffence layers. each layer has own implementation because may be below it don’t have any implementaion reliable.
ARQ Automaic Repeat reQuest protocols
On receiver side:
error detection ( via checksum field)
receiver feedback (ACK = 1 or NAK = 0)
Retransimition : A packet that is received in error at the receiver will be retrans-mitted by the sender TCP have sequence number to indicate piece of packet number
Conclusion
Check-sums, sequence numbers, timers, and positive and negative acknowledgment pack-ets each play a crucial and necessary role in the operation of the protocol
Impovement in tcp
Go-Back-N (GBN) protocol : the sender is allowed to transmit multiple packets(when available) without waiting for an acknowledgment, Selective Repeat (SR) : make sender only resend with specific lost packet instead of all packet in a window size
Connection-Oriented transport TCP
A TCP connection provides a full-duplex service TCP have three-way handshake before 2 end-system can transfer data properly
TCP header structure
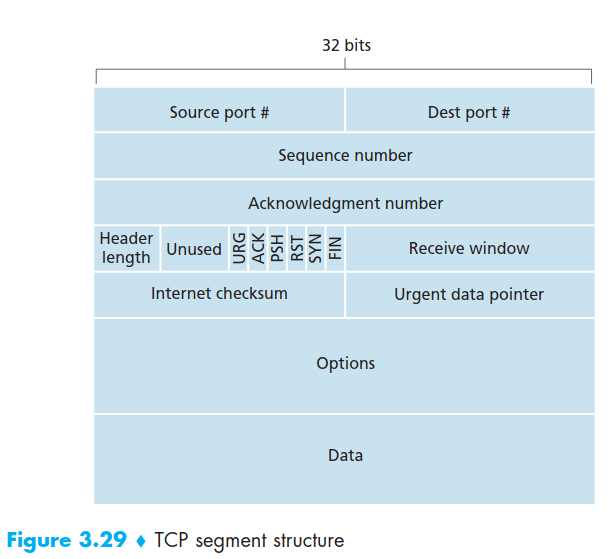
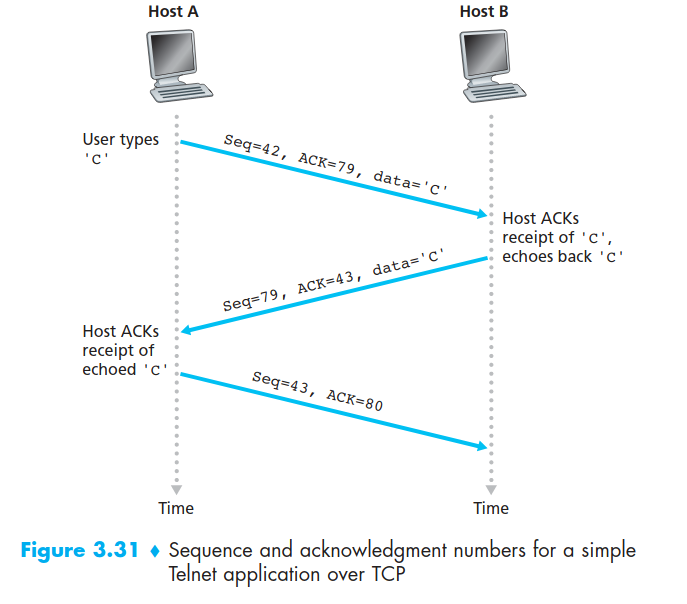
Sequence Numbers and Acknowledgment Numbers
they are 2 of the most important fileds in the TCP segment header.
The sequence number for a segment The acknowledgment number that Host A puts in its segmentis the sequence number of the next byte Host A is expecting from Host B.
Rount Trip Time Estimation and Timeout
the mechanism to recover from lost segments
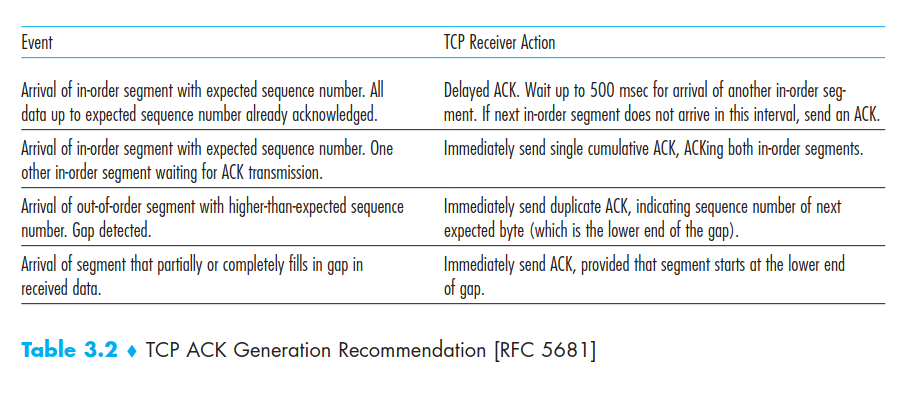
Flow Control
Support if sender send message with speed higher than receiver reading data.
TCP provides flow control by having the sendermaintain a variable called thereceive window. Informally, the receive window is used to give the sender an idea ofhow much free buffer space is available at the receive
TCP connection management
Establish & closing
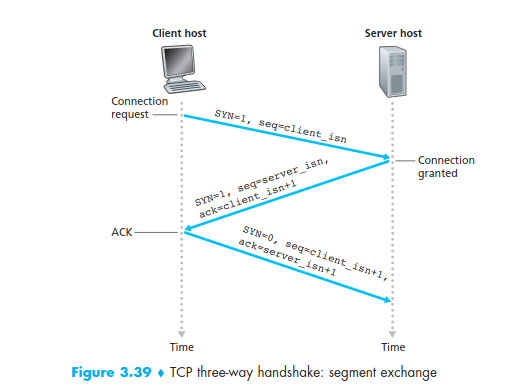
when in the ESTABLISHED state , the tCP client can send and receive TCP segments containing payload
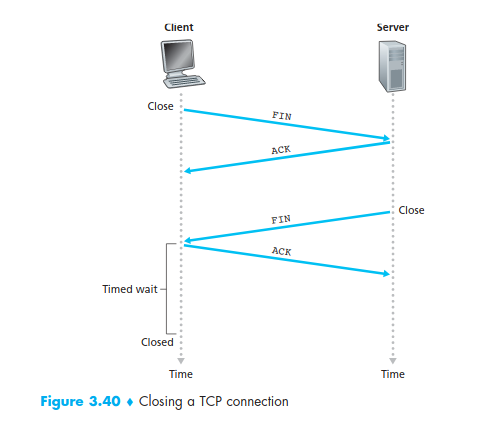
In the case client want to disconnect with server . it need to wait :
- FIN_WAIT1 for ACK from server
- FIN_WAIT2 for FIN from server
- TIME_WAIT for prepare for resend ack if ack is lost ( to server when server resend FIN)
